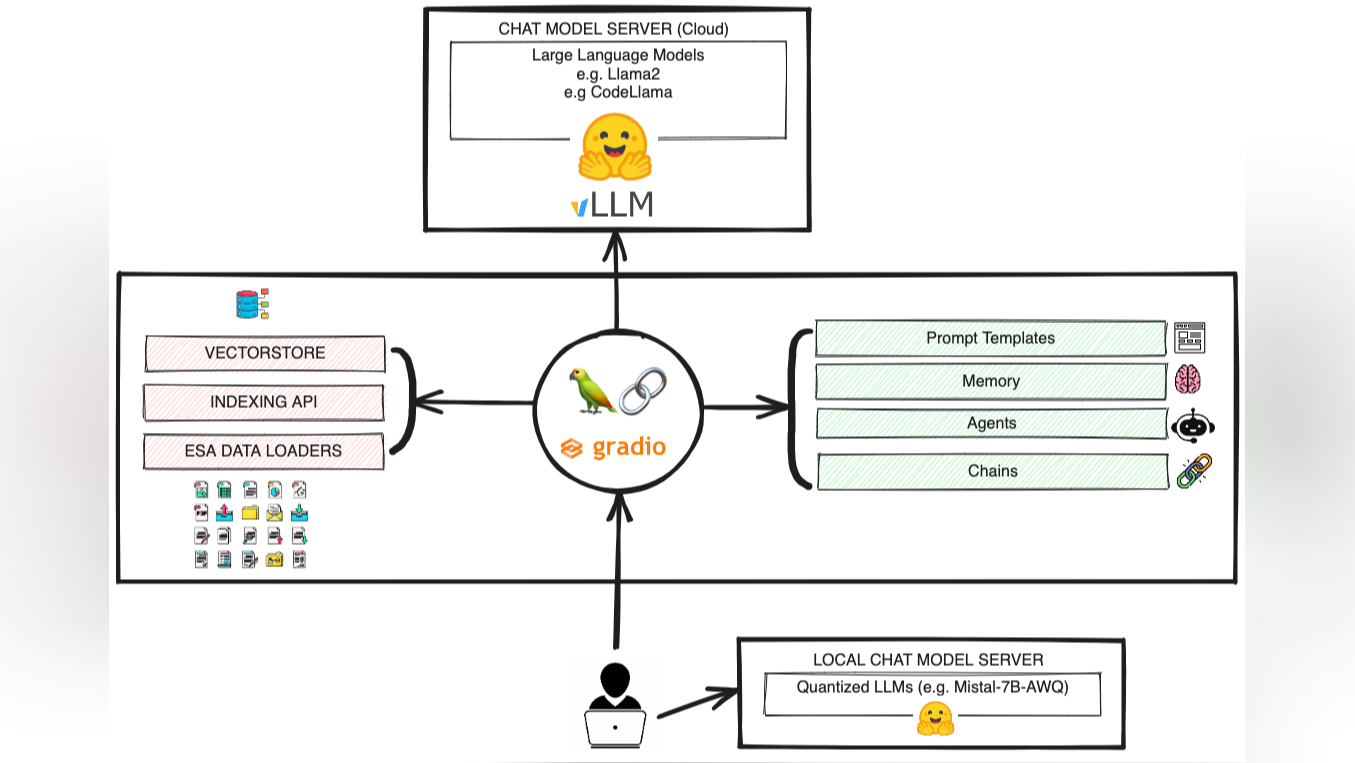
The potential of leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a novel opportunity for enhanced efficiency of software engineering processes. This study proposes an innovative exploration into the utility of open-source LLMs, such as Llama2, Mistral, and CodeLlama, across various stages of the Software Engineering process, specifically tailored for the European Space Agency (ESA) and Space Software projects. Possible use cases include: (1) enhancing requirements elicitation and requirement-related documents review at ESA based on ECSS standards (2) assisting space software developers in writing comprehensive unit tests for test-driven-development (3) accelerating bug analysis and resolution (4) generating in-depth code explanations for improved documentation, knowledge transfer, reusability, and maintenance. The objectives are to select the most value-adding use cases, and to develop an architecture relying on 3 pillars: flexibility, extensibility, and scalability. It will demonstrate performance in a representative ESA environment (cloud and user local machines), assess the capabilities of autonomous agents. The architecture will guarantee data privacy and provide insights into LLM applications across different software engineering phases, modalities and connect LLM to ESA-specific data and code. With the integration of a testbench, we will emphasize on how to foster user trust and empower them. In addition, a comprehensive analysis of the compute resources required for each use case will be performed, including a trade-off of LLMs chat models’ performances for computational effectiveness on GPUs and CPUs. This would pave the way for a similar deployment in ESA’s own cloud and set users’ local machines, adapt to the user traffic, and be extended over time as more use cases are tested or onboarded. The project would use modern libraries such as hugging face, LangChain, and rely on open-source models.