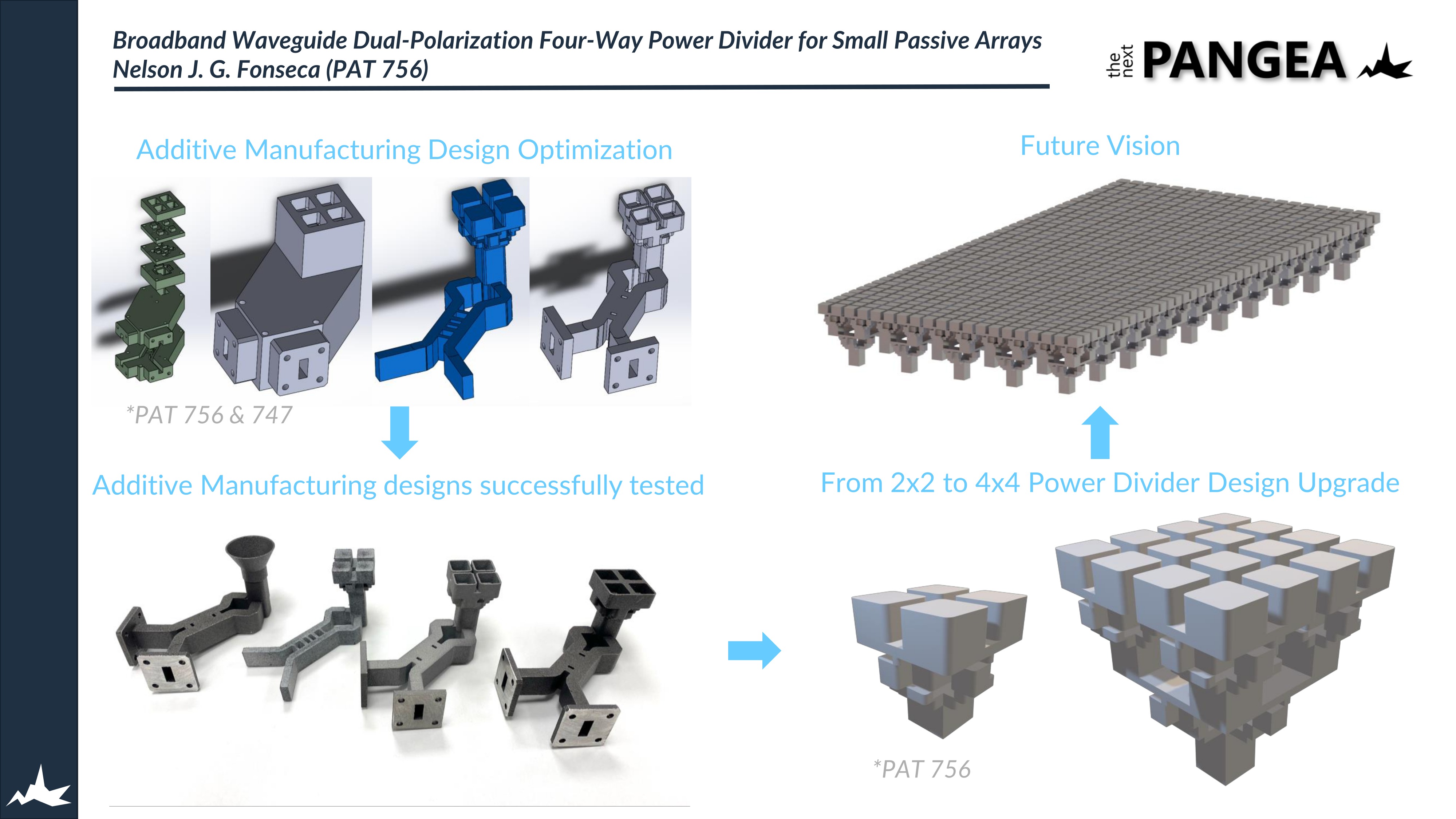
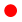
ESA Patent 756 presents a compact dual-polarization four-way power divider, enabling the design of passive waveguide arrays with small element spacing (below one wavelength). That invention was originated as a mean to reduce the length of radiating elements in space-segment feed systems for GEO satellite communication applications, including passive multiple beam reflector antennas and active arrays. This requires compact power dividers, preferably operating in dual-polarization. The next step for extending the already proven four-way power divider is to scale it up to a sixteen-way power divider by combining four four-way power dividers on the top layer, and addressing a fifth power divider, as a waveguide component, for feeding the four top power dividers. As a result, the design will have a single port for feeding and four by four radiating elements. This structure could be joined to an additional component that allows the whole structure to work in dual-polarization. However, there is not any compact solution for waveguide feed chains that does not compromise RF performance. For that reason, there is also a connection with another ESA patent that could fit in this presented idea. ESA Patent 747 presents a two-probe Orthomode Transducer (OMT) or junction (OMJ) which provides high cross-polarization discrimination (XPD) thanks to an asymmetric common waveguide cross-section. The presented idea aims to demonstrate the potential that additive manufacturing has for RF components and space application as well as the potential for the presented power divider as a key component for the ground segment in the satellite communications sector. So, for that reason a single block structure is proposed to be manufactured in advanced manufacturing technologies, such as Laser Powder Bed Fusion or Binder-jetting, to show the capabilities of alternative manufacturing methods in this field.