Running
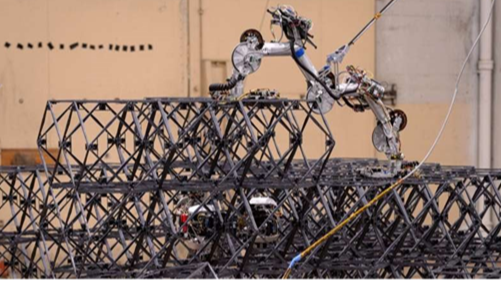
Current methods of assembly rely on human intervention or rigid, predefined sequences, which limit adaptability and increase mission costs and risks. OSTAR-RL aims to overcome these limitations by using reinforcement learning to enable large structures to be assembled by autonomous robots. Aligning with ESA’s vision for sustainable space technologies, paving the way for more efficient long-term space missions & on-orbit assembly, OSTAR-RL will use reinforcement learning to train a robot system to calculate the most efficient assembly sequence in a given set of parameters for the structure and the robots own operating parameters (power, interface points, etc.). We will use a Nvidia Omniverse model followed by validation and verification testing in the In-orbit Servicing Assembly & Manufacturing (ISAM) Facility. OSTAR-RL will demonstrate how autonomous systems can minimise human input into complex assembly sequences whilst providing an efficient and safe operating process.