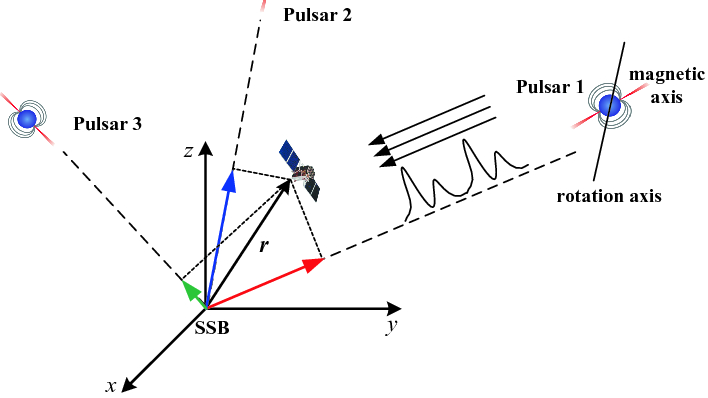
The idea of observing pulsar stars for space autonomous navigation has already caught the attention of several entities, such as ESA and NASA. Driven by the extremely stable and broadband emissions of these celestial sources, many research works and in-orbit demonstrations have been carried out, proving the suitability of pulsars for navigation. However, most of these studies are still based on the X-ray emissions of pulsars, whose statistics (i.e. the photon fluxes) are quite poor. Long observation times and complex (and heavy) on-board instrumentation are typically required, for a positioning accuracy which hardly goes below 10 km. Because of the low number of pulsars emitting in the optical band, the chance of exploiting these emissions has never been considered. Nevertheless, the optical emissions of pulsars show much higher statistics with respect to those in the X-ray band. Such an advantage definitely leads to shorter observation times and simpler (and lighter) instrumentation, suitable for most kinds of mission. The aim of this study is the concept design of a space navigation system for on-board positioning and time synchronization based on optical pulsar signals.