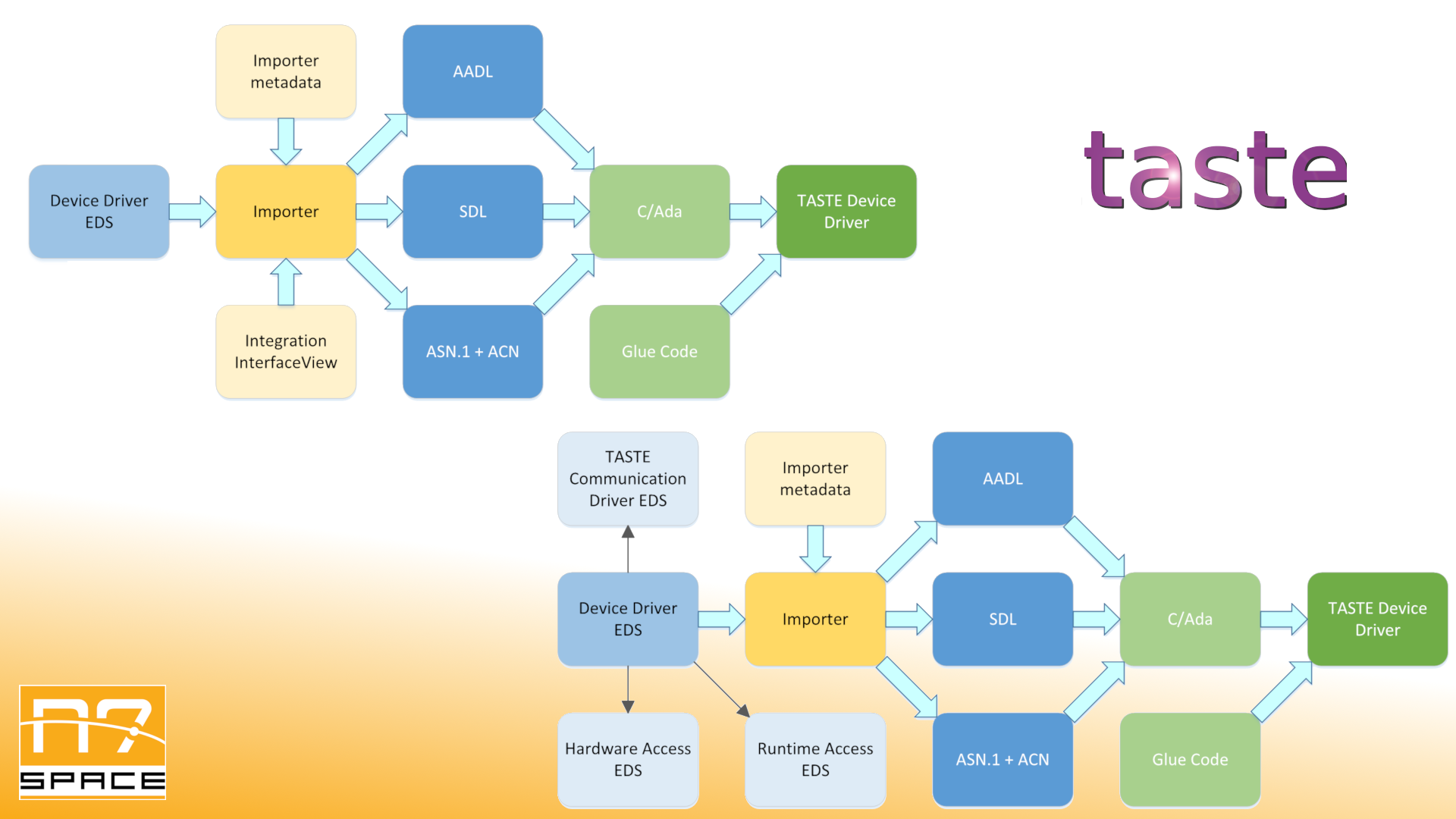
The proposed activity involves a new CCSDS SEDS standard of device specifications, introduced in 2019, and TASTE, ESA’s toolchain for developing embedded software in a model-based (MBSE) approach. SEDS-based driver behaviour specification could be used for automatic code generation of an actual driver or its purely software-based functional mock for use in testing. A major goal of the project is to evaluate such capability by designing an abstract TASTE Communication Driver SEDS. The required driver interfaces could be implemented using concrete SEDS-based device driver specifications, thus providing a way for easy extending TASTE with new communication devices and enriching its ecosystem. To make the solution more practical, a tool for adapting incompatible (on syntactic, and to some extent semantic levels) interfaces using TASTE modelling is to be provided. The tools created during the proposed activity could be incorporated into TASTE, providing a new way of defining used hardware peripherals. Another major goal of the project is to re-use the facilities provided by TASTE to transform SEDS into standalone drivers for use in non-TASTE projects, introducing some aspects of MBSE to now semi-manual code development. For the purpose of testing and evaluation (code size, code quality, performance, completeness) of the generated drivers, N7 Space proposes to re-use a BSP for ARMV71 platform which it created within the scope of earlier ESA activities. Company is also involved in an activity to create tools for importing SEDS models into TASTE as functions, scheduled to start in 2020. Using outputs from both of those activities would provide a good demonstration of MBSE capabilities and validate SEDS suitability for the proposed applications.