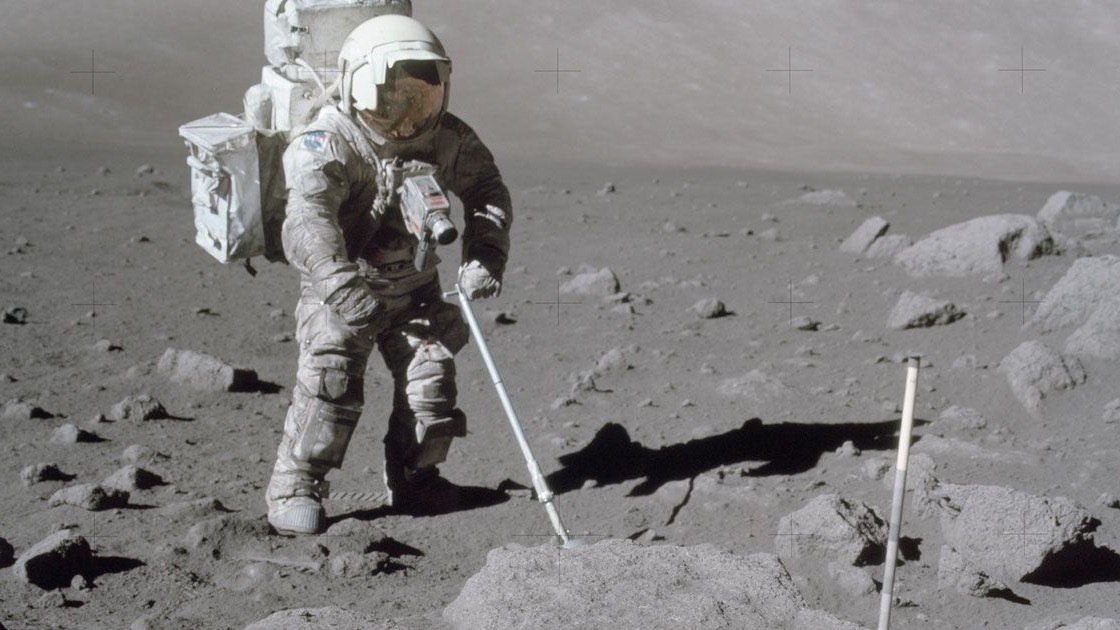
The goals of the proposed project are: 1/ to characterize the interactions among dust particles as well as dust particles with surfaces based on fundamental principles of physics 2/ to improve mission-related applications in space engineering Ground-based spin-in and spin-off fields include the operation and optimization of solar panels in desert areas, as well as general dust mitigation techniques in industry. The study will address Space Exploration concerns by helping characterizing interferences with mechanical, thermal and optical elements of typical surface exploration missions (e.g. Lunar). Dealing with charged dust particles is notoriously difficult in applications, partly because partial fundamental understanding is established on how charging and discharging of dust particles occurs under various environmental conditions. Both passive mechanisms like the exposure to envrionments (UV, plasma etc) might play a role as well as active mechanisms like triboelectric charging. In addition, for space applications also the atmospheric environment may vary from conditions close to Earth, to plasma environments and vacuum conditions. Hence, dust-mitigation known methods to work on Earth may not be sufficient for space; at the same time, novel techniques developed for space have to be thoroughly tested and may well benefit applications on Earth if a better fundamental understanding allow for targeted optimization. The work will involve a combination of modelling and experimental approaches to advance our understanding in a number of directions among i/ the theoretical characterization of perturbed dusty surfaces, ii/ the experimental characterization of crititcal surfaces contamination in vacuum conditions, iii/ the feasibility of electrostatic mitigation techniques in air and in vacuum (e.g. Lunar simulated) environment, iv/ the measurement of fundamental dusty surfaces properties under simulated environments (UV, plasma and electrons irradiation).