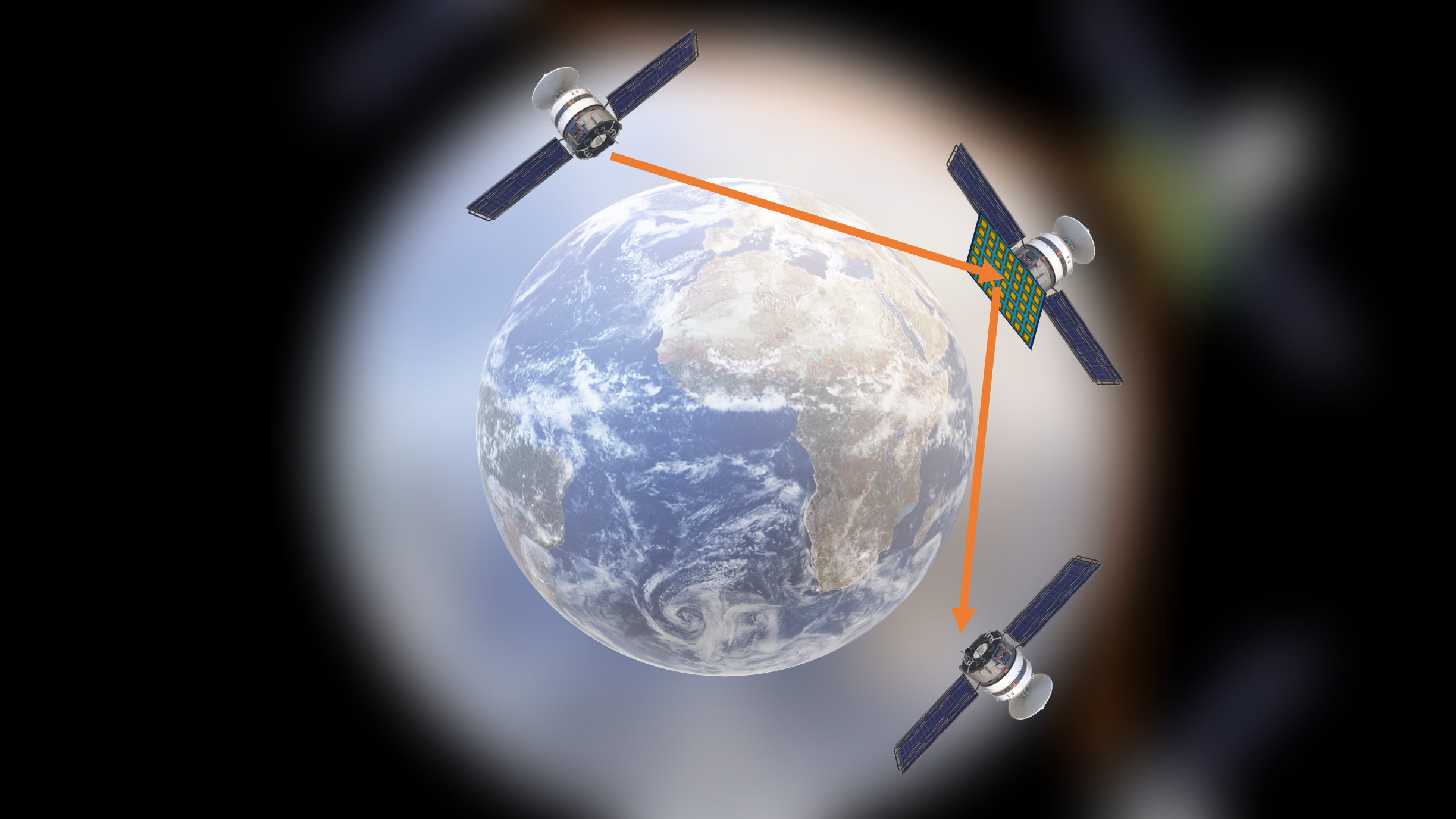
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) refers to a technology that involves deploying a surface composed of intelligent elements, often with the ability to reflect or manipulate electromagnetic waves. These surfaces can be dynamically adjusted to optimize wireless communication in real-time[1][2]. The idea behind RIS is to enhance and control wireless communication by modifying the propagation environment. This can be achieved by adjusting the phase and amplitude of the signals reflected off the intelligent surface. By doing so, RIS can improve signal strength, increase coverage, mitigate interference, and enhance the overall performance of wireless networks. RIS has the advantages of being cost-efficient in comparison to phased arrays[2], since it is composed of passive reflecting elements, resulting in lower manufacturing costs and reduced power consumption. It is also more simple and scalable. It has gained attention as a potential technology for improving the efficiency and reliability of communication systems, especially in scenarios with challenging propagation conditions, and is seen as a promising technique for 5G and beyond, as it can be used to overcome obstacles and optimize signal quality in various environments. RIS has also been considered for the satellite communication to facilitate communication with ground transceivers.
We propose to study RIS as a low-cost option for directing communication, not only to ground, but for inter-satellite communication. These studies are still in a very early stage[3]. Satellites may encounter obstacles or situations that temporarily block or degrade communication signals. RIS could be used to adaptively reflect or redirect signals around obstacles, maintaining more consistent and reliable communication links. Satellites equipped with RIS could optimize communication by dynamically forming and steering beams towards specific ground stations or other satellites, improving overall network efficiency.
[1] E. Basar, M. Di Renzo, J. De Rosny, M. Debbah, M. -S. Alouini and R. Zhang, "Wireless Communications Through Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 116753-116773, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935192
[2] Q. Wu and R. Zhang, "Towards Smart and Reconfigurable Environment: Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Wireless Network," in IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 58, no. 1, pp. 106-112, January 2020, doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107
[3] C. Huang, A. Zappone, G. C. Alexandropoulos, M. Debbah and C. Yuen, "Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces for Energy Efficiency in Wireless Communication ," in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 4157-4170, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609
[4] J. Ye, J. Qiao, A. Kammoun and M. -S. Alouini, "Nonterrestrial Communications Assisted by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces," in Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 110, no. 9, pp. 1423-1465, Sept. 2022, doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2022.3169690
[5]K. Tekbiyik, G. K. Kurt, A. R. Ektı and H. Yanikomeroglu, "Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces Empowered THz Communication in LEO Satellite Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 121957-121969, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3223086
[6] K. Tekbıyık, G. K. Kurt and H. Yanikomeroglu, "Energy-Efficient RIS-Assisted Satellites for IoT Networks," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 9, no. 16, pp. 14891-14899, 15 Aug.15, 2022, doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3112881.