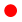
Until recently services from spacecraft at GEO dominated public usage of space. With the launch of the first Starlink spacecraft in 2018 the age of LEO mega-constellations begun: already tens of thousands of planned spacecraft are shifting usage of space to LEO. However, Space Weather (SW) prediction and monitoring at LEO is still inadequate. Most importantly, a normalized index of hardware malfunctions due to SW events does not exist and the relation of malfunctions to SW events is largely qualitative. We propose to introduce a real-time SEE Monitoring System to provide normalized SEU and SEL indices as a function of position and space weather conditions. A polar LEO nanosatellite carrying the following instrumentation will provide comprehensive, normalized monitoring of SW radiation effects: (A) An SEE monitor will provide real-time values of SEUs and SELs for the novel SEU and SEL indices: (A1) An SEU detection scheme consisting of SEU-sensitive memory units of various known LET onset values, developed using hardening by design techniques, will be read continuously by a radiation hardened control Unit. The control unit will recording in real time the number of SEUs that will then be normalized, deriving the SEU index as a function of time, position and SW parameters. (A2) An SEL detection scheme based on a well-characterized analog current monitoring block of a space-qualified Sensor Interface ASIC will detect and record over-currents that may lead to potential latch-ups. (B) A radiation monitor will measure trapped & solar energetic protons with energies from 4 MeV to > 200 MeV as well as the energy and LET spectra of ions. (C) A spacecraft charging monitor will correlate LEO surface charging with auroral precipitating electrons. (D) A magnetometer will monitor field-aligned currents that correlate with enhanced surface charging. (E) A solar cell performance monitor will measure the degradation of solar cell parameters due to the effects of particle radiation.