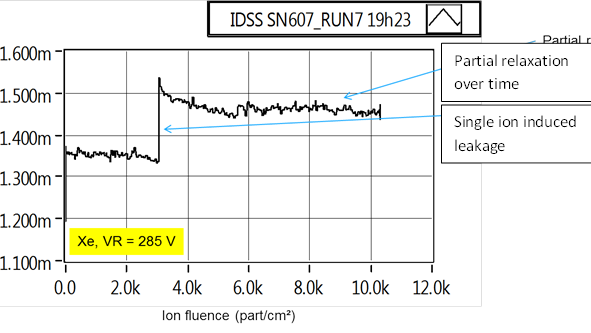
Several studies have demonstrated that Wide Band Gap (WBG) devices can experience leakage behavior under heavy ion irradiation at intermediate voltage. This degradation phenomenon is observed on several wide band gap technologies like Silicon Carbide Diodes, Silicon Carbide MOSFETs, GaN/AlGaN HEMT or Diodes and can potentially stands as a limit to their use for space power applications. Until further improvement of the technology (material, design), the question of this observed effect shall be better quantified against typical spacecraft environment. The study would consider several test candidates and determine a modelling definition of this degradation based on experimental data. Secondly, the study would also evaluate the impact of this degradation on the long term reliability of the semiconductor. This shall be based on the implementation of comparative life-test ageing between irradiated and un-irradiated devices, within a representative application. The results of this characterization will be implemented through worst case analysis in order to benchmark in regards of currently used solutions. Finally, the methodology developed in this study shall be analyzed for potential extension to other technologies sensitive to heavy-ion induced degradation effects. This study shall complete the current European projects (H2020 Call, GSTP) that strive for developing a European independent access to key technologies such as wide band gap electronics that are identified in our technologies roadmap.