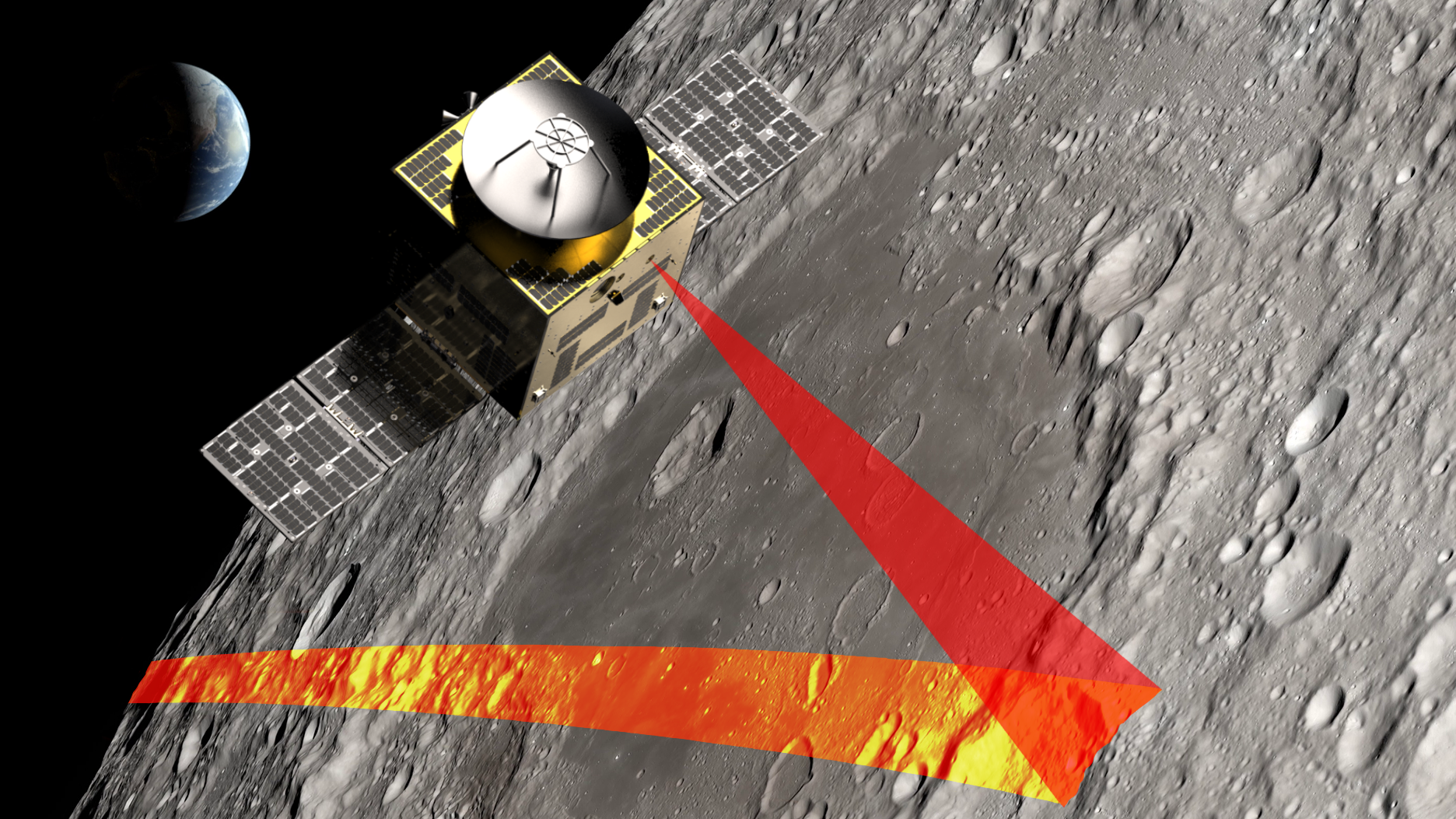
The Moonraker mission will fly a spacecraft equipped with a LiDAR payload in a polar orbit about the Moon. During its 3-year mission, Moonraker will achieve the following objectives: 1. Wide-area mapping of the lunar polar regions and other regions of interest with 4 m ground sampling distance (GSD), <1 m vertical accuracy, and <1 cm precision. Data from these scans will be used to identify candidate landing sites and base locations for future lunar surface missions, and provide an unprecedented data source for lunar science and exploration. 2. High-resolution mapping of specific landing sites and other areas of interest with 0.5 m GSD, <1 m vertical accuracy, and <1 cm precision. Data from these scans will enable mission planners to study final landing sites in detail, assessing them for hazards and other risk factors, science opportunities, and operational conditions for surface activities. LiDAR data will be downlinked directly to Earth and processed to produce state-of-the-art 3D Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) of the lunar regions most critical for future human exploration.