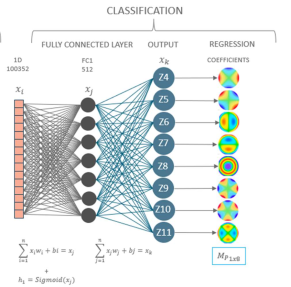
A new wavefront sensing technique, can be applied for WFE detection and for in flight wavefront correction of future large space telescopes (if used within an active optics correction chain together with a deformable mirror). This activity develops a novel data retrieval method and to proof the feasibility of a wavefront sensor. The new method provides the opportunity for a novel wavefront sensor, which can be simple, very small, and robust. Compared to the classical methods of wavefront sensing, a simple and low-cost hardware solution with only one optical element and a 2D detector is found. Implemented within a space telescope it provides an in-flight monitoring and correction of optical aberrations and by that, allowing low mass and low volume telescope designs with reduced costs, by still providing a high optical performance.
The current challenge for such a sensor is to find a retrieval method to infer the distortion of the wavefront from the digital data acquired by the detector. A retrieval algorithms will be explored and coded. A laboratory breadboard of such a sensor will be built as well as the related OGSE. Such OGSE will serve as testbed for the sensor and the code. As far as we know, such a miniaturized sensor has never been built before and no dedicated data retrieval method exists. From that perspective both hardware and software are completely new and feature a high potential to improve or even enable future space missions for astronomy and for Earth observation with optical apertures never realized before. Starting TRL: 2. Target TRL at the end of the activity: 3.