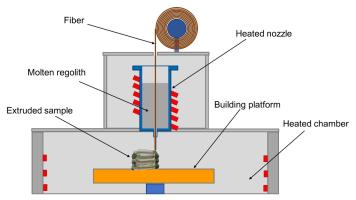
Currently, different Additive Manufacturing (AM) techniques such as solar and laser sintering have been studied in order to fabricate various test geometries and demonstrators for lunar applications; however, the fabricated objects underwent crack formation; thus, they present inadequate mechanical properties for functional use. In this project, we propose to study the regolith material in detail for direct melt-Fused Layer Deposition (FLM) application in which the molten lines of regolith undergo the required annealing process layer by layer. In this technique, lunar regolith could be melted inside a heated kiln embedded in a build chamber with controlled heating and cooling rates, which avoid the crack formation of the final products. Molten lines will be deposited in a layer-wise manner and the quality of the final products will be evaluated and compared to the ones fabricated using solar and laser radiation. This technology could be an appropriate AM candidate for lunar applications based on the following points:
- The use of controlled heating and cooling rate of the material avoids crack Formation and distortions Controlled viscosity during the print
- There is no need for binder; thus, the direct use of the lunar regolith with no additional material transport from Earth is possible
- The technology is compatible with lunar conditions (temperature, atmosphere and gravity)
- The technology enables lunar fiber and filament fabrication